Post Categories

A Breakdown Of What Makes A SharePoint Site
Introduction to a typical SharePoint Site Collection
For beginners, understanding the basic structure of a SharePoint site is essential to effectively use its features and organize content. A SharePoint site is organized in a hierarchical and modular way, making it easy to navigate and manage.
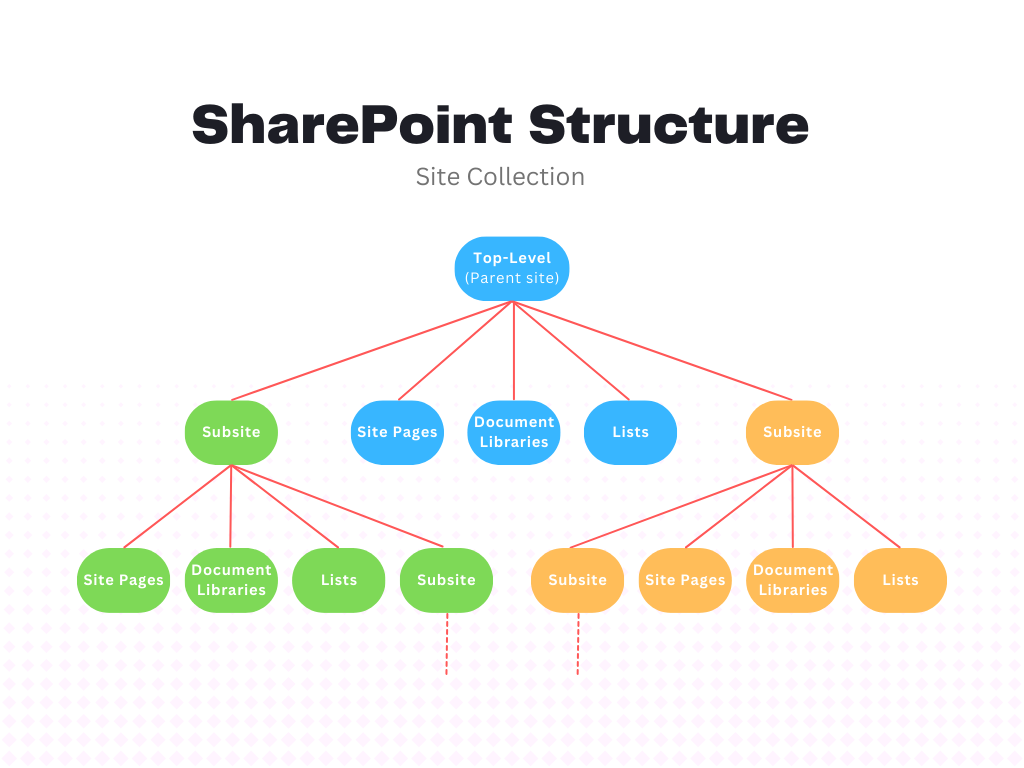
At the top of this structure is the Site Collection, which acts as a container for all sites within an organization. Within a site collection, the Top-Level Site serves as the main entry point, providing access to all subsites and shared resources. Subsites are specialized sites created under the top-level site, often used for specific departments, projects, or teams.
Each site contains various Content Areas such as Document Libraries for storing files, Lists for managing data, and Pages for displaying information. User Permissions are set to control who can access and edit content, ensuring security and proper management.
By understanding these fundamental components, beginners can effectively navigate and utilize SharePoint to enhance collaboration and productivity within their organization.
Key Components to a SharePoint Site Collection
Site Collection
At the top of the hierarchy, a site collection is a group of sites that share common settings and resources. It provides a unified framework within which various sites can be created and managed. Each site collection serves as a distinct entity with its own set of permissions and settings.
Top-Level site
The top-level site, often referred to as the root site or parent site, is the main entry point for the site collection. It acts as a central hub, providing access to all subsites and shared resources. This site typically contains important information and navigation links that are relevant across the entire site collection.
Subsites
Subsites are individual sites created within the top-level site. They can be tailored to specific departments, projects, or teams, allowing for specialized content and functionality. Subsites inherit certain settings from the top-level site but can also be customized independently to meet unique needs.
Content Areas
SharePoint sites are comprised of various content areas that organize and manage different types of information:
- Document Libraries: Specialized repositories for storing and managing documents and files.
- Lists: Structured collections of data, similar to spreadsheets, used for managing items such as tasks, contacts, or events.
- Site Pages: Web pages used to display content and information within the site. Site Pages can be customized with various web parts to present dynamic content like news, calendars, and reports.
- Web Parts: Reusable components that can be added to pages to display specific types of content and functionalities, enhancing the site’s interactivity and usability.
User Permissions
SharePoint employs a robust security model that allows precise control over who can access and modify content. Users can be assigned different permission levels based on their roles:
- Site Owners: Users with full control over the site, including the ability to manage settings, permissions, and content.
- Site Members: Users who can contribute and edit content within the site.
- Site Visitors: Users with read-only access, allowing them to view content without making changes.
- Custom groups and roles can be created to allow for more specific needs.
- Active Directory Security groups can also be used in SharePoint permissions.
Customization and Branding
SharePoint sites can be customized and branded to align with the organization’s identity and requirements. This includes applying themes, customizing layouts, and utilizing site designs to create predefined configurations and functionalities.
Integration and Collaboration Tools
SharePoint seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft tools, enhancing collaboration and productivity. Key integrations include:
- Microsoft Teams: For team collaboration and communication.
- Power Automate: For automating workflows and business processes.
- Power Apps: For creating custom applications within SharePoint.



